Integrated Command and Control Center for Sustainable Smart Cities
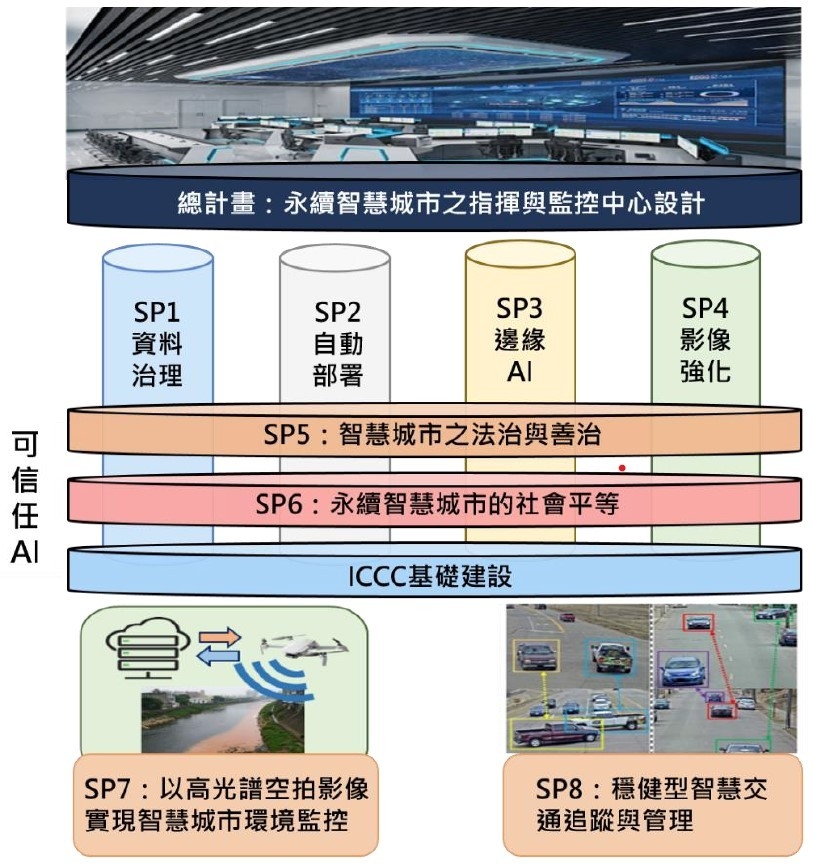
Urbanization brings about convenience and economic benefits to life, but at the same time, it also brings numerous management and survival challenges. Sustainable development is a major global concern, and the United Nations has established 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The development of smart cities is also in response to various issues caused by rapid urban growth, such as traffic congestion, poor air quality, inadequate medical resources, diminishing water supplies, and difficulties in waste management. Overall, the quality of environmental living in urban areas is inferior to non-urban areas.
In light of the aforementioned issues, this project proposes the design of an Integrated Command and Control Center (ICCC) for a Sustainable Smart City. The center aims to capture real-time information on various aspects of the city and make accurate and effective decisions in real time.
Smart Observer: Fishermen Work Hour Estimation using AI and Statistical Analysis
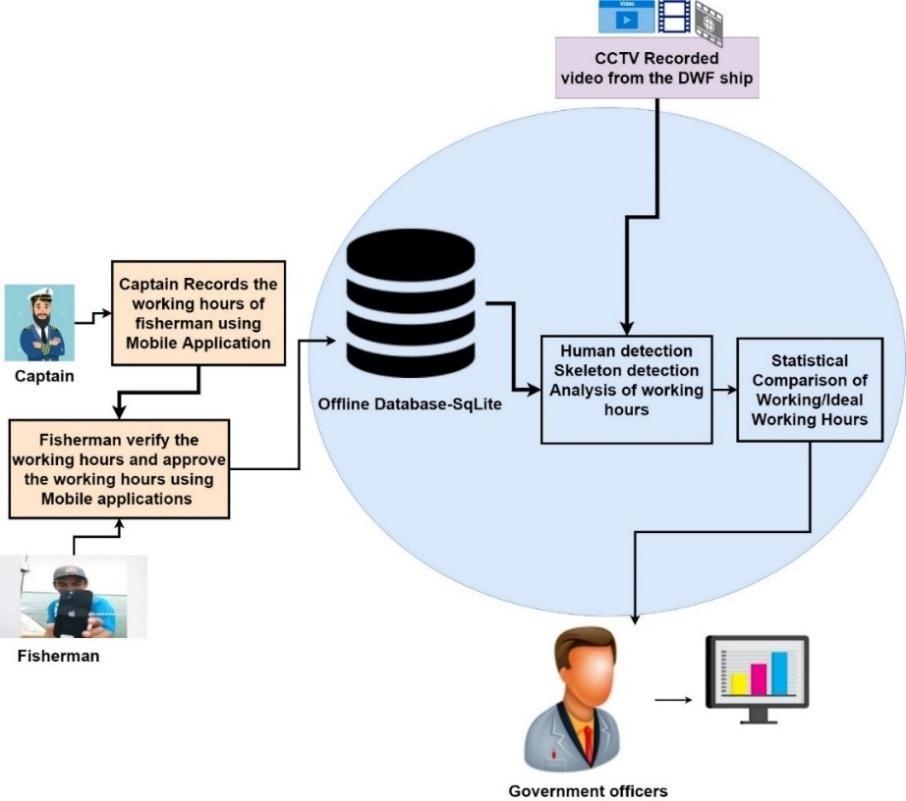
The issue of labour exploitation is a growing concern for human rights. Taiwan boasts one of the world’s largest fleets of distant water fishing (DWF) vessels, generating a market worth 40 billion NT dollars with 1,000 ships. Despite this impressive economic value, there have been reports of foreign fishers being exploited.
Fishermen working on these vessels are often subjected to long working hours, low wages, and poor living conditions. These conditions can lead to physical and mental health problems, exploitation, and abuse.
We proposed a system addresses labour exploitation in Taiwan’s DWF industry and aligns with Sustainable Development Goals by promoting decent work and economic growth. It also improves working conditions to safeguard fishermen’s physical and mental health.
Movement Disorder Evaluation for Parkinson's Disease Patients
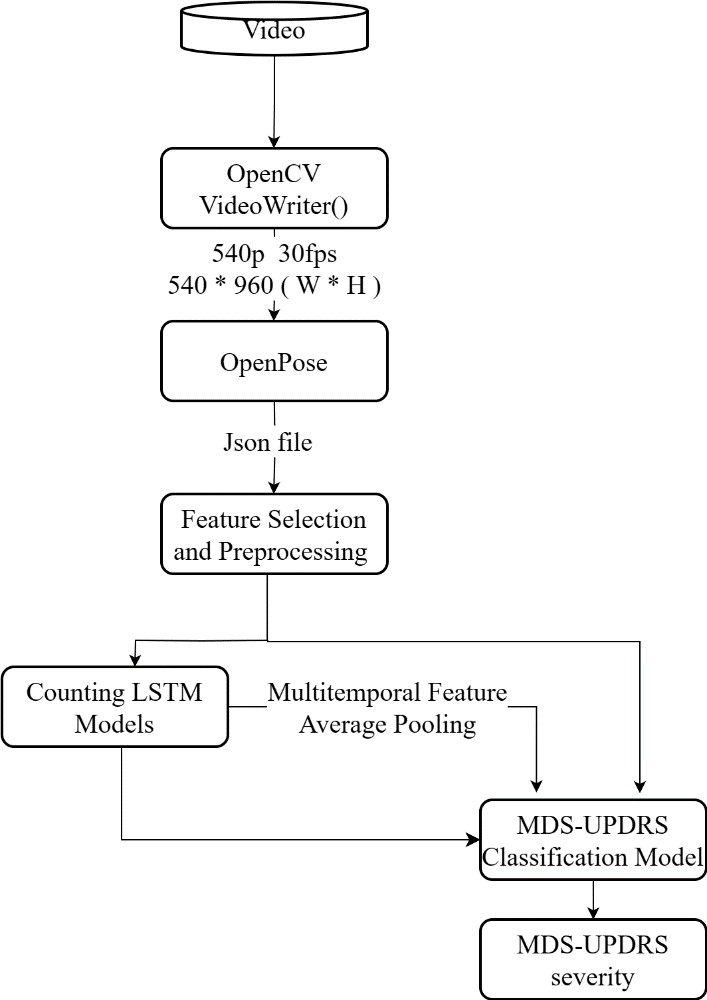
Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects the motor nervous system, with symptoms including tremors, rigidity, reduced motor function, and abnormal gait. However, diagnosing the disease currently relies on subjective clinical assessments, highlighting the need for objective diagnostic tools.
In recent years, remote healthcare technology has gained popularity, enabling online consultations and treatment, particularly useful during the COVID-19 pandemic. We have explored visual imagery-based assessments using computer vision and artificial intelligence to analyze patients' movements and postures. This approach eliminates the need for specialized sensors and utilizes regular camera equipment, making it cost-effective and convenient.
The study aims to develop a visual imagery method based on smart mobile phones, using the OpenPose technique to extract joint point features from videos. This vision-based approach leverages the prevalence of smartphones in Taiwan and is well-suited for the post-COVID-19 era, offering a promising direction for Parkinson's disease evaluation and management.
Cyber-Physical Systems Design
Due to the wide range of applications and high heterogeneity of Cyber-Physical Systems(CPS), system developers is hard to design among different domains in last few years. The main objective of our research is to propose a generic architecture for the CPS. The purpose of our first year research is to design a common platform which can be reused in the new application areas based on our CPS design experiences in four different application. In second year, we'll implement the proposed architecture design.In third year, we will present and design processing kernels of CPS.
Following section shortly describes our researches in four different CPS applications.
Smart Grid Design
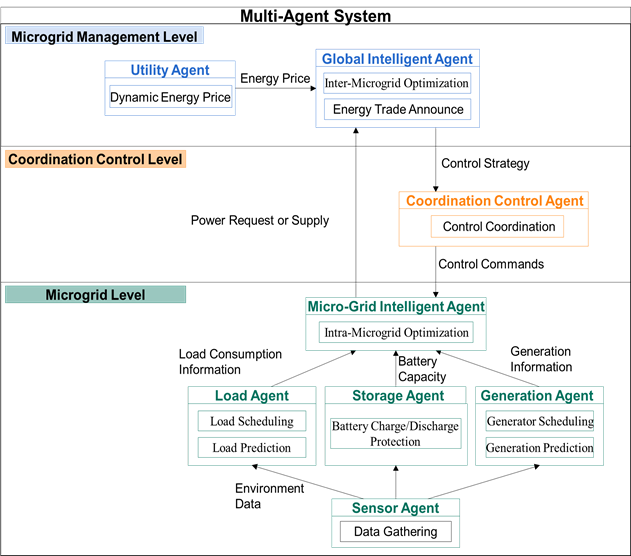
With the rapid growth of electricity demand, there is an increasing electricity generation burden on the centralized power system. To address this issue, the architecture of smart grids has been proposed. A smart grid is composed of a market, a utility, one or more micro-grids, transmission lines, and distribution lines. The power and the bidding information can be exchanged in a smart grid. When there is a shortage of electricity in a micro-grid, this grid can buy electricity from the utility or from other micro-grids. On the contrary, when the electricity in a micro-grid is self-sufficient, this grid can sell the excess electricity to the utility or the other micro-grids.
In the design of a micro-grid, it comprises renewable resources, energy storage systems (ESS), and loads. Using renewable resources can help reduce the carbon pollution. But the generation capacity of renewable resources is affected by climate change and environmental changes, resulting in non-stability of power generation. Because of the intermittent renewable resources, it is difficult to maintain the power stability. Thus, the ESS plays an important role in satisfying user daily requirements and emergency situation. For example, if the utility interrupts the power supply under abnormal conditions, the ESS can be an emergency power system.
An important issue in an advanced distribution management system for smart grids is how to accurately predict future power generations and load demands because without such prediction distribution could be inefficient.
Further, for a stable and reliable smart grid, it must ensure that the power supply is sufficient for all micro-grids. Generally, power shortage is not allowed in smart grids, except in the case of power plant accidents. Therefore, on the condition of satisfying the given power demands, the goal is to reduce overall cost in the smart grids.
We propose a multi-agent system based smart grid framework, which provides not only a fair energy allocation mechanism for micro grids, but also the piecewise linear regression for prediction. To implement a simulation environment for real smart grid operation, we adopt the Java Agent DEvelopment Framework (JADE) toolkit to simulate the multi-agent based micro grids, and use Matlab/Simulink simulation platform to design and implement power generators and power loads.
Related Publications:
Model Predictive Optimization for Distribution Management in Smart GridHierarchical Optimization of Smart Grids with Energy Storage Systems - A Model-Predictive Control and Auction-based Method
A cyber-physical system framework for smart grid wireless communications
A knowledge based approach for selecting energy-aware and comfort-driven HVAC temperature set points
Sensing-driven energy purchasing in smart grid cyber-physical system
Smart Traffic

In recent years, with increase in the number of vehicles, more and more traffic issues are becoming the focus of attention worldwide. One of the most important problems is traffic congestion. Currently, most traffic systems still use fixed-time setting for a very long cycle. These systems cannot dynamically adjust traffic light timing in response to unexpected situations such as traffic accidents, natural calamities, or sudden incidents. With advances in technology, traffic data such as traffic volume, speed, and waiting time can now be gathered by sensors or cameras.
Leveraging on automatic traffic data collection we try to address the traffic congestion issue by proposing a novel Model Predictive Control (MPC)-based Traffic Light Control System (MTLCS). MTLCS includes a traffic flow prediction model and a traffic timing optimization method. Historical traffic data is used to predict future traffic volumes. An MPC-based traffic light optimization method is proposed to obtain appropriate time settings that can reduce overall congestion. Our method also has the ability to dynamically adjust traffic signal timings. It can rapidly respond to real-time traffic conditions to reduce traffic congestion.
Related Publications:
Dynamic Traffic Light Optimization and Control System using Model-Predictive Control MethodAdaptive Timing Optimization for Cyber Physical Signal Control System
A traffic congestion control method in the cyber physical systems
Cyber physical system - smart cloud traffic control
The modeling and simulation of vehicle distance control based on cyber-physical system
Driver Fatigue Prediction
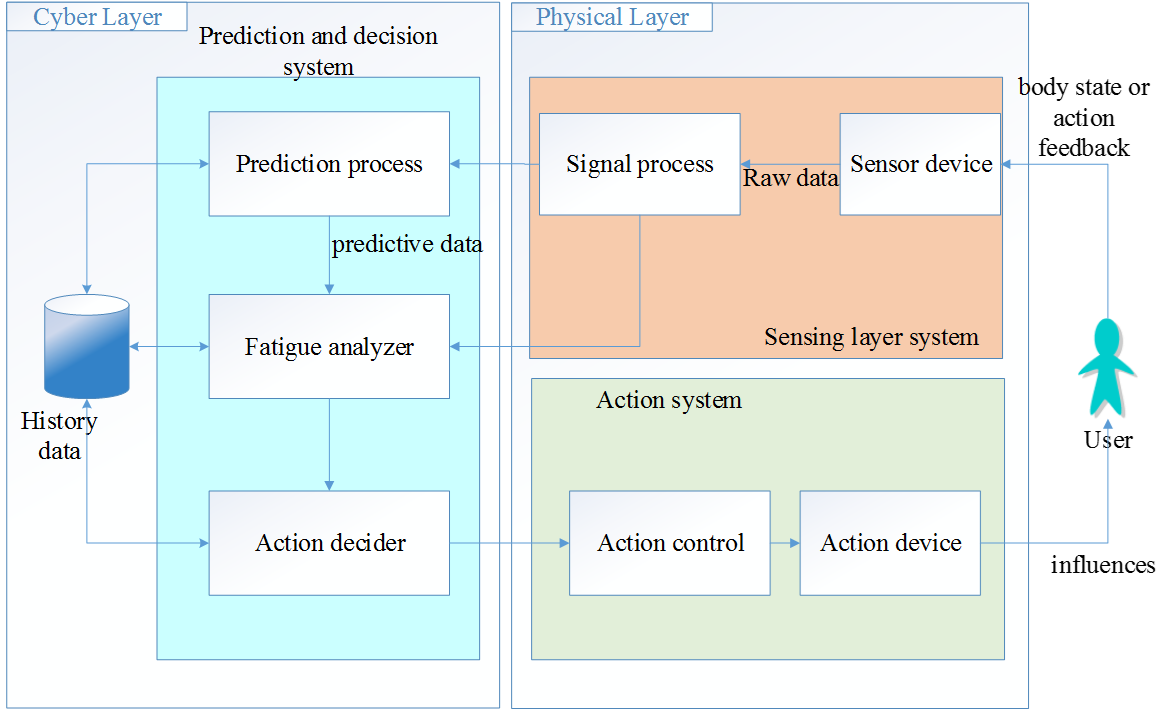
The driver's fatigue is one of the main causes of traffic accidents. Fatigue declines driver's responsiveness and attention that leads to dangerous driving behavior. This could raises the risks to driver itself and other pedestrians. If it is possible to detect the driver's fatigue immediately while driving, the driver is cautioned and warned other passers-by to be vigilant to increse overall safety of the traffic. It is urgent to design a complete fatigue driving detection system.
Most of the fatigue driving detection systems considers the fatigue accidents as a result of fatigue had been caused that leads to accidents.These studies mainly focus on detecting the current fatigue situation of driver. Therefore, even if the the system issued a warning can not guarantee whether the driver has energy to respond to the warning.
Fatigue changes over time. Thereby, our study hopes to design an innovative prediction model based on the previous changes of drivers in fatigue and to predicts when will the driver be tired and can not driving normally. In order to improve traffic safety, we can obtain some reaction time in advance for drivers to plan the parking loaction to rest.
Related Publications:
A New System for Driver Drowsiness and Distraction DetectionAn Integrated Health Management Process for Automotive Cyber-Physical Systems
Assessment of mental fatigue during car driving by using highresolution EEG activity and neurophysiologic indices
Landsilde Prediction
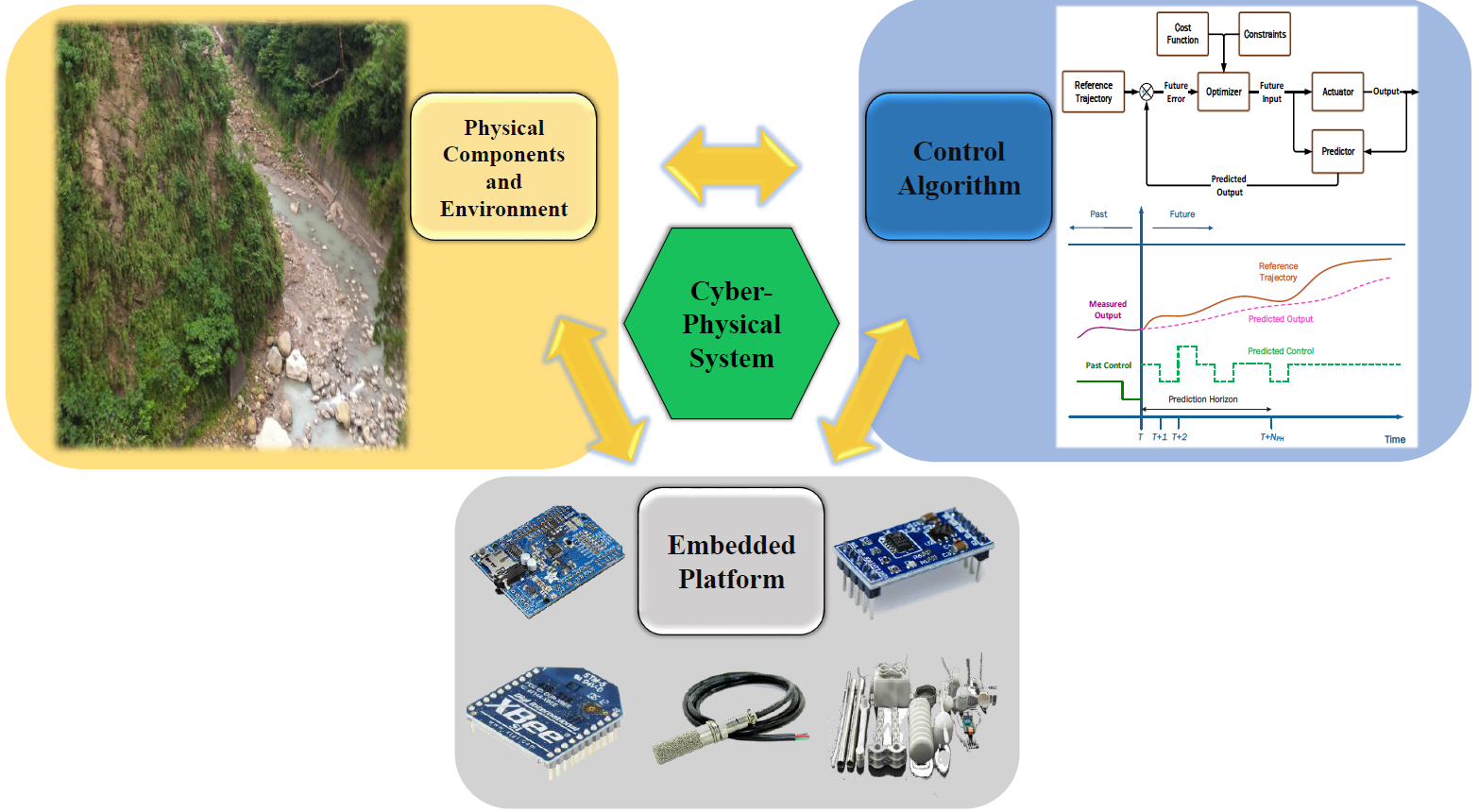
Landslide is one of the natural disasters that could cause huge damages to properties and great loss of life. Many approaches are proposed to detect landslide and monitor them. Though landslide detection could be done in real-time, there is still not enough time to adopt any reacting policy to keep human life and properties safe. In order to minimize the extent of losses caused by landslides, prediction and pre-alarm of the occurrence of landslides are necessary. The main concern of a prediction system is to predict precisely. Thus, a well design prediction model is critical. However, the natural environment keeps changing with time and the environmental information is complex and changing. The learnability and adaptability of the prediction systems become critical features to guarantee prediction accuracy. According to the above mention requirements of the prediction, artificial neural networks (ANNs) is a good solution to provide accurate prediction and high learnability in its train phase. A suitable architecture of ANN promotes the prediction accuracy. We design a Cyber Physical System (CPS) of landslide prediction. The CPS can be sensitive to the environment changing and provide a suitable control by well analyzing the data from different kind of sensors. Thus, the energy saving and accurate prediction are guaranteed simultaneously.